Agronomy & Forestry
Scientific equipment plays a pivotal role in modern agriculture by
enabling precise analysis, optimization, and management of
agricultural processes.
Research and Monitoring
Applications
Soil Analysis: Devices like soil testers measure pH, moisture, and nutrient levels, helping farmers optimize soil fertility for specific crops.
Plant Growth Studies: Growth chambers provide controlled environments to study plant development under varying conditions.
Genetic Engineering: Tools like PCR machines and centrifuges are essential for genetic modification, enabling the creation of pest-resistant and drought-tolerant crops.
Water Quality Testing: Analyzers assess water samples for turbidity and nutrient content, ensuring efficient irrigation practices.
Precision Agriculture: Equipment such as leaf area meters and climate monitoring systems help monitor crop health and environmental conditions, improving yield and sustainability.
These technologies are transforming agriculture into a more efficient and sustainable practice.
Laboratory equipment is fundamental in genetic engineering for crops, playing a crucial role in every stage of the process.

DNA Extraction: Equipment like centrifuges and micro-pipettes are used to isolate and extract DNA from plant cells, which is the first step in genetic modification.

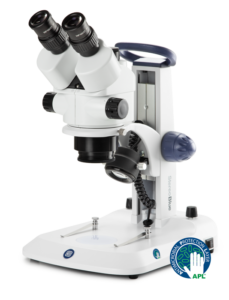
Microscopes: High-resolution microscopes monitor cellular and molecular changes during the engineering process.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR machines amplify specific DNA sequences, enabling scientists to focus on genes of interest for modification or study.
Gel Electrophoresis: This technique, using specialized apparatus, separates DNA fragments by size to confirm successful amplification or isolation of the desired gene.
Gene Editing Tools: Technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 are employed in labs to edit genes with precision. Lab equipment such as electroporators helps introduce the edited genes into plant cells.
Tissue Culture Systems: Growth chambers and sterilized laminar flow hoods are used to culture genetically engineered plant cells, allowing them to develop into full plants under controlled conditions.

This equipment enables scientists to create crops that are pest-resistant, drought-tolerant, or nutritionally enhanced. It’s a fascinating intersection of biology and technology!
